Tara is a recent addition to our solutions team as a trainee. She holds an MSc in Finance and has a strong dedication to both investments and sustainability.
To provide a clear overview of the key developments in energy security and infrastructure in Europe, we have created a timeline highlighting the major events from 2022 to 2025:

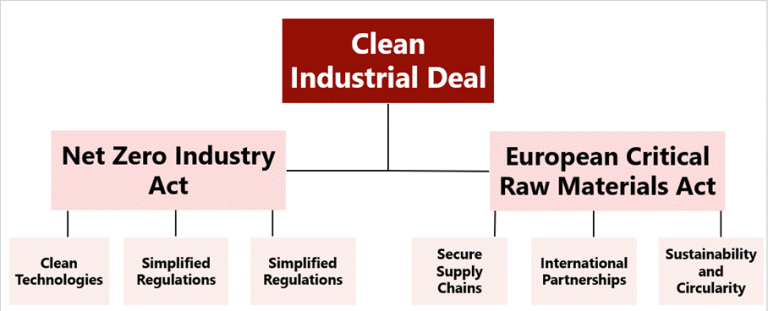
Clean Industrial Deal
The European Commission addresses the urgent need to reduce energy costs, enhance energy security, and promote sustainable industrial practices across the EU. By focusing on clean technology, circularity, and reducing dependencies on third country suppliers for raw materials, the Clean Industrial Deal aims to create a competitive and resilient market.
The Clean Industrial Deal outlines several key measures designed to support energy intensive industries such as steel, metals, and chemicals, which face high costs, unfair global competition, and complex regulations. By focusing on clean technology, circularity, and reducing dependencies on third country suppliers for raw materials, the Deal aims to create a competitive and resilient market.
The Industrial Decarbonization Accelerator Act will increase demand for EU made clean products by introducing sustainability, resilience, and a 'made in Europe' criteria in public and private procurements. The Deal also proposes the establishment of a EUR 100 billion Decarbonization Bank to support clean manufacturing and innovation.
The Clean Industrial Deal has two main components: the Net Zero Industry Act and European Critical Raw Materials Act.
Net Zero Industry Act: This act aims to scale up the manufacturing of clean technologies in the EU, including solar photovoltaic, wind energy, batteries, and carbon capture and storage. It simplifies the regulatory framework, attracts investments, and create better market conditions for clean tech in the EU[1].
European Critical Raw Materials Act: This act focuses on ensuring a secure and sustainable supply of critical raw materials necessary for the green and digital transitions. It aims to strengthen domestic supply chains, reinforce international partnerships, and promote sustainability and circularity in the raw materials sector[2].
The Clean Industrial Deal represents a significant step forward in the EU's efforts to achieve a sustainable and competitive industrial sector, ensuring that European industries can thrive in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Infrastructure Package in Germany
Following the Clean Industrial Deal, Germany has announced a significant infrastructure package aimed at revitalizing its economy and enhancing energy security. This package includes a EUR 500 billion fund dedicated to various sectors such as transportation, energy, education, and defense. By addressing long-standing infrastructure deficits, Germany aims to promote economic growth and ensure a resilient energy system.
This infrastructure package is a major development for several reasons. This makes a significant shift in Germany's fiscal policy. Traditionally, Germany has adhered to a strict "debt brake" (Schuldenbremse), a constitutional rule that limits new government borrowing to 0.35 per cent of GDP. The amendment to this rule allows for greater fiscal flexibility, enabling substantial investments in critical infrastructure. This change is expected to boost Germany's competitiveness and support its transition to a low-carbon economy [3].
The EUR 500 billion funds will be distributed over a 12-year period. Key areas of investment include the energy transition, with a focus on renewable energy sources, energy efficient building renovations, and the expansion of electric mobility infrastructure. Significant funds will be directed towards modernizing transportation networks, enhancing digital infrastructure, and improving education and healthcare facilities.
Germany's infrastructure package is also part of a broader European trend. Several EU countries are implementing similar measures to address infrastructure deficits and promote sustainable growth. For example, France and Italy have announced large-scale investment plans focused on green energy and digitalization. These coordinated efforts across Europe aim to strengthen the EU's overall economic resilience and accelerate the transition to a sustainable, low-carbon future[4].
In our view, Germany's infrastructure package is a bold step. By investing in critical sectors and modernizing its infrastructure, Germany is positioning itself to better compete in the global economy. The focus on sustainability and energy security aligns with broader EU goals, potentially setting a precedent for other countries to follow. This comprehensive approach not only addresses immediate economic challenges but also lays groundwork for long-term growth and stability.
The Importance of Energy Security
Energy security is becoming a paramount driver in the transition to cleaner energy sources. Rather than climate concerns, the quest for security is now the main impetus behind this shift. Nations are increasingly creating a diversified energy mix to insulate themselves from geopolitical, macroeconomic, and financial risks.
In a report from Carlyle, “The New Joule Order”, suggests that the one significant aspect of this transition is the concept of "Peak Oil Trade," where the focus shifts from the availability of oil to the security of energy supply. As nations prioritize energy security, there is an increasing demand for non-fossil fuels. This trend a more profitable, cleaner, as well as a faster transition to renewable energy.
According to Carlyle's report, during the energy security era (1973-1993) following an oil crisis, the transition to nuclear and renewable energy sources progressed at a similar, if not slightly faster, pace compared to the Net Zero 2050 era (2014-2024). The former period saw a reduction in fossil fuel consumption from 94 per cent to 85 per cent of total joule consumption. In contrast, the Net Zero 2050 era achieved a decrease from 85 per cent to 81per cent. This comparison highlights that prioritizing energy independence can drive a more rapid energy transition than focusing solely on environmental concerns or economic efficiency.
Emphasis on Energy Security
The emphasis on energy security is also reshaping the landscape of decarbonization and energy investment. For example, tariffs and border adjustment taxes can incentivize secure, localized energy production. This is analogous to carbon tax and a green premium and may be more effective at spurring energy transitions[5].
Recent Power Outage
The recent power outage across Spain and Portugal on April 28, 2025, further highlights the importance of energy security. This major blackout, which lasted for about ten hours in most areas, caused severe disruptions in telecommunications, transportation systems, and essential services[6]. The incident underscores the need for a resilient and diversified energy infrastructure to prevent such widespread impacts in the future.
Impact of Global Events
The COVID-19 pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine have underscored the critical importance of energy security. The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages and delays, and highlighting the risks of over-reliance on imported fossil fuels. Similarly, the invasion caused severe energy shortages and price spikes in Europe, emphasizing the need for energy independence. These events have accelerated the push for renewable energy sources, demonstrating that energy security is a key driver in the transition to cleaner energy.
REPowerEU Plan
The REPowerEU plan, launched by the European Commission in May 2022, is another critical initiative aimed at enhancing energy security and accelerating the transition to clean energy. This plan was developed in response to the energy market disruptions caused by Russia's invasion of Ukraine and focuses on reducing the EU's dependence on Russian fossil fuels by diversifying energy supplies, increasing energy efficiency, and accelerating the deployment of renewable energy sources[7].
Electrotech Strategy
The report, "Energy Security in an Insecure World", written by Ember, highlights the importance of Electrotech as a new strategy for energy security. Electrotech is the practical application of electricity in technology, with key technologies such as electric vehicles, heat pumps, and renewables which can significantly reduce fossil fuel imports and minimize security risks. According to Ember, ElectroTech can slash imports and minimize security risks through three key levers: electric vehicles, heat pumps, and renewables. These technologies can cut net fossil fuel imports by 70 per cent, saving importers USD 1.3 trillion per annum globally[8]. By shifting energy supply to local renewables and directing energy use toward domestically generated electricity, nations can achieve energy independence.
Benefits for Our Clients
While the narrative around ESG has shifted and discussions about climate have taken a step back, the challenges and real-world effects of climate change remain significant. As the world deglobalizes and countries focus more inwardly, this creates challenges in terms of trade and vulnerable value chains. However, as highlighted in this Solution Spotlight, the shift in focus from climate to security can lead to similar or even stronger outcomes for energy transition.
Energy security is a critical advantage, as diversifying energy sources and investing in renewable energy can reduce the risk associated with geopolitical uncertainties and fluctuating fossil fuel prices. When combined with energy storage and a more resilient grid, this approach may ensure a more stable and secure energy supply. While renewable energy investments have shown volatility, they can also present significant long-term growth potential and opportunities for innovation. The focus on AI and clean technology within the Clean Industrial Deal and Germany's infrastructure package may drives innovation and efficiency.
Importance for Our Portfolio and the World
The themes of energy security, technological development, and sustainable growth are highly relevant globally. By focusing our portfolios on these areas, we can address critical challenges such as climate change, energy security, and economic resilience. We believe that companies in these sectors may benefit significantly from investments directed towards solving these challenges.
Energy powers modern society, driving economic growth and enhancing quality of life. Energy security reduces dependence on unstable regions, mitigates supply risks, and ensures stability. Renewable energy diversifies supply, reduces imports, and provides stable costs. It also promotes sustainability and public health. While renewable technologies often rely on imports, they require minimal maintenance once installed. Fossil fuels, though storable, need continuous importation, which is vulnerable to geopolitical tensions.
At the Summit on the Future of Energy Security held in London this April, energy sector leaders emphasized the importance of a broader and more resilient approach to energy security. The event, co-hosted by the IEA and the UK Government, brought together decision makers from 60 governments and over 50 major energy companies. The summit highlighted the need for international cooperation to ensure secure, affordable, and sustainable energy supplies. Keynote speeches underscored the evolving nature of energy security and the necessity for collective action in a rapidly changing world[9].
The Clean Industrial Deal and Germany's infrastructure package create new opportunities for investment in sectors such as renewable energy, electrification, and energy storage.




